Blogs
- Oct 16, 2023
- Blog
- Service
Toward the Realization of a Next-Generation Mobility Society: SoftBank's Blueprint
#Connected
Scroll
What is SoftBank's Vision for a Next-generation Mobility Society?
In recent years, with the widespread adoption of cellular communication technologies such as 5G, there are high expectations for the application of communication to various industries and objects, not limited to smartphones. SoftBank has been engaged in research and development since 2017 with the assumption that communication technology will be applied to vehicles and transportation infrastructure.
SoftBank and Honda to Begin Joint Research on Connected Car Technologies that Utilize 5th Generation Mobile Communication System (5G)
In particular, communications for automobiles are being actively discussed in society. With the evolution of autonomous driving and ADAS(Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems), how to utilize communication has become very important. SoftBank is promoting various activities under the concept of “next-generation mobility society”, i.e., a society that realizes optimization not only for automobiles but also for entire roads through communication. By sharing information with each other through communication between traffic participants (e.g., pedestrians, vehicles) and transportation infrastructure, we aim to reduce traffic accidents and realize a society in which traffic participants can move more safely.
Components of the Next-generation Mobility Society
In the next-generation mobility society, the following factors need to be considered.
● Traffic participants
○ Car
○ Motorcycle
○ Bicycle
○ Pedestrian
● Transportation Infrastructures
○ Road
○ Traffic light
○ Roadside sensors such as fixed cameras
Traffic participants include a variety of people, such as cars, motorcycles, pedestrians, and bicycles, depending on the means of transportation and the situation. Transportation infrastructure includes elements that build a transportation society, such as roads, traffic lights, and roadside sensors.
Traffic accidents are caused by operating errors and carelessness to the road ahead, and ignoring traffic lights and crossing the road for pedestrians and bicycles. In order to avoid them, it is difficult to respond to all traffic situations and blind spot areas with only the sensing functions installed in automobiles.
Therefore, it is necessary for traffic participants to collect data on themselves and the surrounding environment, and for transportation infrastructure to collect data by observing traffic conditions and traffic participants from a third-party perspective, and communication is important for linking these data. There are different types of data, such as vehicle information, pedestrian location information, and detection data from sensing devices, and different communication requirements vary accordingly. Consequently, a network that satisfies them stably is required. SoftBank is working with partners to consider what kind of network it should be based on these components.

Cellular V2X as the Core Technology
Cellular V2X has two modes of communication operation: PC5 for direct communication and Uu for indirect communication. PC5 is a communication method that allows direct communication between devices, and includes Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) and Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I), and Vehicle-to-Pedestrian (V2P) communications. Uu is a communication method that communicates via a base station, and provides Vehicle-to-Network (V2N) communication.
The key for the next-generation mobility society is not a system centered on vehicles, but a system in which transportation participants and transportation infrastructure cooperate with each other. In order to realize such a system, it is very important to utilize Uu in combination with PC5. By grasping traffic conditions from a bird's-eye view, it is possible to call attention to appropriate traffic participants.
Along with the popularization of devices such as smartphones, base stations used in Uu play a role as social infrastructure such as economic activities and lifelines. In particular, the fact that various things can be connected to the network and can be used nationwide simply by installing a device on a vehicle is characterized by a lower hurdle to social implementation than other communication standards.

SoftBank's vision of the role of Uu in the next-generation mobility society can be summarized as follows:
・Eyes and ears expansion
・Brain expansion
・Sharing perceptions
"Eyes and ears expansion"
Vehicles have many sensors such as camera, LiDAR, and radar. Their detection range is about 100m. For example, if there are other vehicles rapidly approaching from a distance within that range, the vehicle must brake suddenly to ensure safety. By sharing information among traffic participants, it is possible to send danger notifications to smartphones, extend the detection range of sensors installed in vehicles, and supplement blind spots. In this way, it acts as an expansion of the vehicle's eyes and ears and enables one to see the situation in a bird's-eye view.
"Brain expansion"
Vehicles are equipped with computers that make decisions based on information obtained from sensors. In the future, computers will require extremely complex processing to achieve autonomous driving and advanced ADAS. By sending vehicle data to the network, it is also possible to make decisions to high-power computers located in data centers. In this way, brain expansion means the selection of the right place to analyze and process information. By flexibly selecting different computational resources, such as servers in the cloud or in the Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC), depending on the requirements of the application, it is possible to support tasks that were previously difficult to handle by vehicles alone.
"Sharing perceptions"
Sensor information obtained from transportation infrastructure will increase in the future. By having a control tower that centrally manages them, it is possible to share information that could not be obtained by one's own vehicle alone, i.e., perception. By aggregating information from multiple points, more advanced analysis is possible, and appropriate information can be provided for traffic participants facing various situations.

Examples of SoftBank's Activities
SoftBank conducts joint research with companies that play a key role in the next-generation mobility society and conducts research and development of communication systems. In this article, we will introduce two examples.
Activity with Suzuki
In this activity, we collaborated with Suzuki Motor Corp. to conduct a use case verification aimed at reducing accidents during right turns at intersections.
When a vehicle turns right at an intersection, if there is a vehicle in the oncoming lane, there is a risk that a collision may occur because the straight vehicle moving in the oncoming lane cannot be detected visually and by sensors. In this use case, vehicles near an intersection use Uu to send location information and vehicle information to the MEC server, which links each vehicle information and map information to manage it. If the MEC server determines that there is a risk of collision by performing collision detection based on the aggregated vehicle information, it transmits the collision detection result to the target vehicles to avoid a collision accident when turning right.
Driving assistance systems, such as collision avoidance, typically rely on standalone systems within individual vehicles, utilizing onboard sensors like cameras and radars. However, in this verification, we confirmed the substantial utility of a system that leverages "Brain expansion" by opting for the MEC server as a computational resource and "Sharing perceptions" through distributing results derived from the centrally managed information on the MEC server.

Reference: Use Case Verification in Collaboration with Suzuki to Reduce Accidents during Vehicle Right Turns at Intersections by Utilizing 5G SA and Cellular V2X Technology
Activity with Honda and Central Nippon Expressway
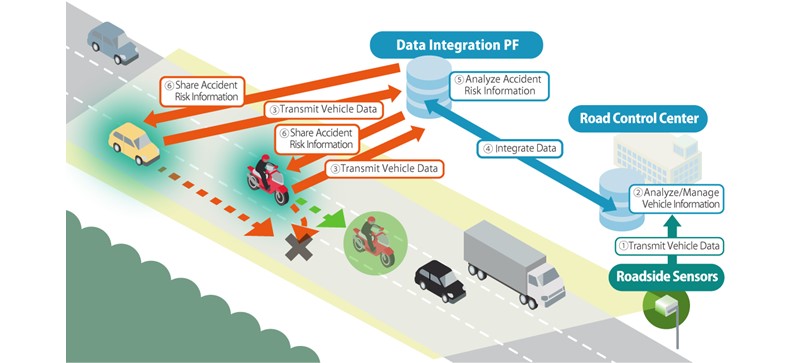
In this case activity, we collaborate with Honda Motor Co., Ltd., Honda R&D Co., Ltd., and Central Nippon Expressway Co., Ltd. to conduct a use case verification whether it is feasible to enhance information gathering and provision through cooperation between automobiles and roadside sensors.
In this use case, vehicles with communication capabilities (i.e., connected cars) transmit vehicle information such as the location and speed to the data integration platform in real time via Uu. Meanwhile, roadside sensors installed on the expressway also detect vehicle information, including vehicles without communication terminals (non-connected cars), and send this data to the control center. By integrating information between the road control center and the data integration platform, we facilitate road-vehicle coordination. This involves analyzing and assessing the risks of traffic accidents and encourages actions to preemptively avoid accidents by notifying nearby vehicles of anticipated risks such as sudden lane changes.
In these demonstrations, we plan to verify the feasibility of "Eyes and ears expansion" by acquiring information from the transportation infrastructure that could not be known by vehicles alone and to verify the feasibility of "Sharing perceptions" that aggregates various information on the platform to make a judgment.
Reference: Initiating Verification of Use Cases for Accident Risk Prediction and Information Notification through Traffic Infrastructure Information Collaboration Utilizing Cellular V2X
Through these initiatives, we will continue to clarify the issues required for networks in the next-generation mobility society and develop technologies.