

Promoting “Net Zero”
throughout the supply chain
In addition to its existing “Carbon Neutral 2030” declaration, which aims to reduce GHG emissions (“Scope 1” and “Scope 2”) from business processes and energy consumption to zero by 2030, SoftBank will work to remove supply chain emissions (“Scope 3”), which includes GHG emissions generated by business partners, in our group companies, by 2050.

Efforts toward Net Zero
Transitioning to 100%
renewable energy
for all electricity
use by FY2030
The Company aims to transition all electricity used in its business operations to renewable energy by FY2030. In addition, more than 50%* of the total will be procured from renewable energy sources as we advance initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.


[Note]
- * The total of SoftBank Corp. and Wireless City Planning Inc.
Long-term renewable energy procurement contract
We aim to procure all the electricity required for our telecommunications business from renewable energy sources in the future by gradually increasing our procurement of renewable energy.
We will contribute to achieving our carbon neutrality and realizing a decarbonized society by entering into long-term renewable energy procurement contracts and reducing greenhouse gas emissions by sourcing more than 50% of the electricity we use from renewable energy by FY2030. Furthermore, long-term procurement contracts will encourage the transition to a business structure that is less susceptible to the impact of rising electricity costs.
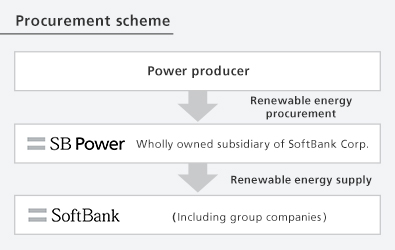
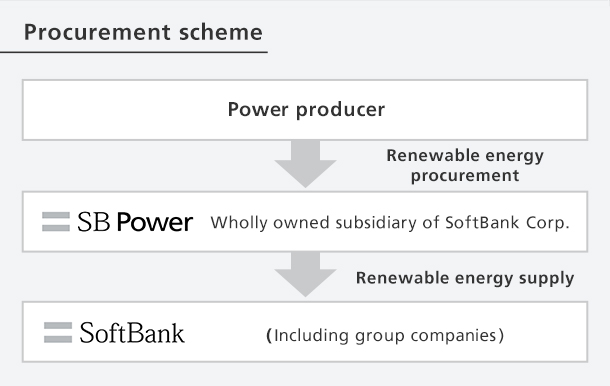
Shift to renewable energy for power used at base stations
SoftBank Corp.'s main business is the mobile communications business. The annual greenhouse gas emissions from our business activities total approximately 620,000 tons CO2 equivalent (FY2024 results), more than half of which is attributable to power use at base stations across Japan. Our total annual greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are equivalent to those of approximately 250,000 ordinary households. In order to reduce GHG emissions, we have decided to switch to electricity from renewable energy supplied by SB Power.* In FY2024, 92.6% of base station power came from renewable energy.
SoftBank Corp.'s main business is the mobile communications business. The annual greenhouse gas emissions from our business activities total approximately 620,000 tons CO2 equivalent (FY2024 results), more than half of which is attributable to power use at base stations across Japan. Our total annual greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are equivalent to those of approximately 250,000 ordinary households. In order to reduce GHG emissions, we have decided to switch to electricity from renewable energy supplied by SB Power.* In FY2024, 92.6% of base station power came from renewable energy.
In addition, the Company launched a demonstration project in Ichihara, Chiba Prefecture in 2026 for base stations that generate their own renewable energy from solar and wind power. By covering about one third of the electricity needed to operate the base stations through on site generation, the Company reduces CO2 emissions. By utilizing these base stations, the Company increases the ratio of renewable energy used at its base stations and establishes a new model for decarbonizing telecommunications infrastructure.

In addition, the Company launched a demonstration project in Ichihara, Chiba Prefecture in 2026 for base stations that generate their own renewable energy from solar and wind power. By covering about one third of the electricity needed to operate the base stations through on site generation, the Company reduces CO2 emissions. By utilizing these base stations, the Company increases the ratio of renewable energy used at its base stations and establishes a new model for decarbonizing telecommunications infrastructure.
[Note]
- * Electricity supplied from effectively 100% renewable energy, with zero net CO2 emissions, achieved by combining non-fossil certificates designated as renewable energy.

Energy-saving measures utilizing cutting-edge technologies
Power efficiency utilizing
AI, IoT, etc.
It is said that the impact on the global environment can be predicted by utilizing AI, IoT, big data, and other cutting-edge technologies to analyze the massive amount of environmental data through AI learning features. In order to become able to implement various countermeasures based on those predictions, the world's attention is focused on the application of cutting-edge technologies to environmental problems.
In 2026, the Company developed an AI driven system that dynamically manages sleep mode control for base stations to maximize power savings and began deploying it at a portion of its sites.
This system reduces power consumption by automatically shifting selected cells to sleep mode during low traffic periods while maintaining communication quality.
Going forward, the Company will further leverage cutting-edge technologies and synergies between group companies to achieve power efficiency in our facilities and equipment and implement measures to reduce the environmental load.
Reducing the environmental load through the development of next-generation batteries
We are striving to reduce the environmental load through research and development aimed at the development and practical application of next-generation batteries. Power consumption is increasing through the evolution of devices, which is leading to an increase in CO2 emissions. Increasing the capacity and energy density of batteries equipped in devices can enhance the performance and efficiency of devices and equipment and reduce the load on the environment.
Moreover, the “SoftBank Next-generation Battery Lab” was established in June 2021. In October 2021, in collaboration with Empower Greentech Inc. of the U.S., we succeeded in demonstrating a lightweight, high-capacity, high mass energy density lithium metal battery whose mass energy density is more than twice that of conventional batteries (520 Wh/kg class).
By encouraging research development and early commercialization, we aim to serve as a platform to promote the development of next-generation batteries.




Realizing a communications infrastructure
with a low environmental load
HAPS (High Altitude Platform Station) is a telecommunication platform located in the stratosphere at an altitude of approximately 20 km. Its closer proximity to the ground compared to GEO and LEO satellites allows for low-latency communication. By utilizing batteries and solar power, we aim to provide stable communication services and flight, and reduce environmental impact.
High Altitude Platform Station “HAPS”


Other initiatives
The Company's stance
on the use of carbon credits
Endorsing the Paris Agreement's goal of a decarbonized society by 2050, we have positioned climate change response as a strategic priority.
The Group has set a target of achieving net zero greenhouse gas emissions across our entire value chain by 2050 and is actively pursuing it.
Referencing the SBTi (Science Based Targets initiative) guidance, The Group gives top priority to maximizing greenhouse gas reductions across Scope 1, 2, and 3.
Regarding remaining carbon emissions, we are both promoting insetting—by investing in carbon absorption and removal activities throughout and outside our supply chain—and evaluating the use of carbon credits for offsetting.
We recognize that, depending on their type, both carbon insetting and carbon credits can effectively support ecosystem restoration and sustainable community development, and consider them initiatives that contribute to our nature-positive goals alongside our climate change measures.
The Group takes a multifaceted view of increasingly diverse and complex environmental and social challenges, and is dedicated not only to reducing emissions across our supply chain but also to contributing to the global decarbonized society.
Approach to carbon credit utilization
General policy
Regarding the use of carbon credits, The Company emphasizes high quality in procurement and generation, and also considers impacts on biodiversity, local communities, and human rights, as well as co-benefits.
Also, The Company recognizes that carbon credits must not cause negative social or environmental impacts and must possess high reliability, transparency, and sustainability.
The Company's perspective
on carbon credit deployment
- Project Types: The relevance between project types, such as carbon removal, absorption, and storage, and our business activities is considered when selecting credits.
- Additionality: Credits must be generated through carbon removal, absorption, or storage activities that would not occur without the project.
- Permanence: Credits must include mechanisms ensuring long-term preservation of carbon removal, absorption, or storage activities.
- Double-Counting Prevention: There must be a system in place to ensure the same emission reductions are not claimed by multiple entities.
- Transparency: Credits should be subject to proper disclosure or third-party monitoring.
- Reliability: Credits must be underpinned by valid and dependable data, calculation, and verification methods.
- Governance: Credits must be supported by appropriate risk management and an operational framework.
Initiatives related to
Scope 3 reduction
As part of our efforts to reduce Scope 3 emissions, we are also considering measures such as offsetting credits, permanent carbon removal, forest carbon sequestration, and oceanic carbon uptake in cases where complete elimination of emissions is not achievable. We have endorsed the establishment objectives of the CO2 Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) Consortium, which was created by the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology to conduct research and development on CO2 capture, utilization, and storage technologies. Our participation aims to contribute to the overall improvement of industry-wide technologies.
Additionally, we have joined as an initial member of the Natural Capital Credit Consortium (NCCC) and aim to promote forest conservation by contributing to the creation of carbon credits through the utilization of IT.
As part of the effort to reduce overall CO2 emissions of society, we have launched the “Future and Coral Project” in collaboration with Okinawa Onna Village, which actively promotes coral planting and environmental conservation, along with numerous companies and organizations. Through the conservation activities of coral reefs, we contribute to the promotion of CO2 absorption in the oceans by restoring marine ecosystems.
Furthermore, our group company, SB Power Corporation, offers a household electricity plan called “Shizen Denki”, which has zero CO2 emissions. For each contract, SB Power Corporation contributes 50 yen per month as an activity support fund, providing support for forest conservation activities.
Additionally, we have started calculating the carbon footprint for some of our products, and we plan to expand this assessment to cover more products in the future.
Forest Conservation Support Project
for Prefectures Nationwide
The Company is carrying out the “Forest Conservation Support Project for Prefectures Nationwide” to promote environmental conservation and contribute to achieving a decarbonized society by supporting forest conservation efforts in all 47 prefectures and cities across Japan.*
Through this initiative, the Company plans to donate more than 4 billion yen via Japan's corporate hometown tax program and collaborate with local governments over a 15-year period from 2025 to 2040 to sustain forest restoration through tree planting. This contribution will result in the planting of roughly 1.8 million trees if all funds are allocated to reforestation.
[Note]
- * Comprising 46 prefectures and Hachioji City, Tokyo.
NatureBank
“NatureBank” is a consumer-participation reforestation program that visualizes and encourages eco-friendly behavior. It covers 16 eco-actions offered by the Company and its Group companies, creating a mechanism that enables people to see and feel how their daily eco choices contribute to the environment. The Company plants trees to offset the CO₂ emissions reduced* through these 16 actions—matching the equivalent CO₂ absorption of the planted trees. The more consumers engage in eco-friendly actions, the more trees are planted, increasing collective contributions to forest conservation.
[Note]
- * CO₂ reduction and absorption figures are estimated by the Company based on publicly available data from the government and each participating company.
Environmental data
We collect and publicize data on energy usage and greenhouse gas emissions in the appropriate manner.
Resource usage /Greenhouse gas emissions
Our greenhouse
gas emission reduction targets
certified by
the
science based targets
initiative


Material issue for leading response
to climate change
"Contributing to
the Global Environment
with the Power of Technology"
-


Contribute to mitigating climate change, promoting a circular economy and the adoption of renewable energy by utilizing cutting-edge technologies to pass on a sustainable global environment to the next generation.
Contributing to the Global Environment with the Power of Technology
