With the spread of generative AI, power consumption at data centers is rapidly increasing. For example, training GPT-4 requires over 50 gigawatt-hours (GWh) of electricity, the equivalent to the monthly electricity usage of about 55,600 average households in the US.
By contrast, the human brain operates on a mere 20 watts of power and can perform a wide variety of complex tasks. Compared to generative AI, the amount of data needed by the human brain for learning new tasks is also significantly lower, highlighting its high learning efficiency and adaptability.
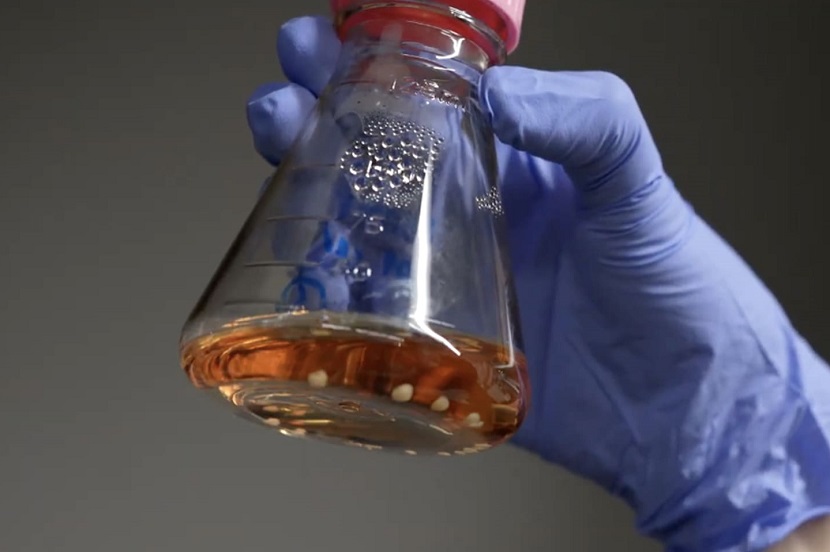
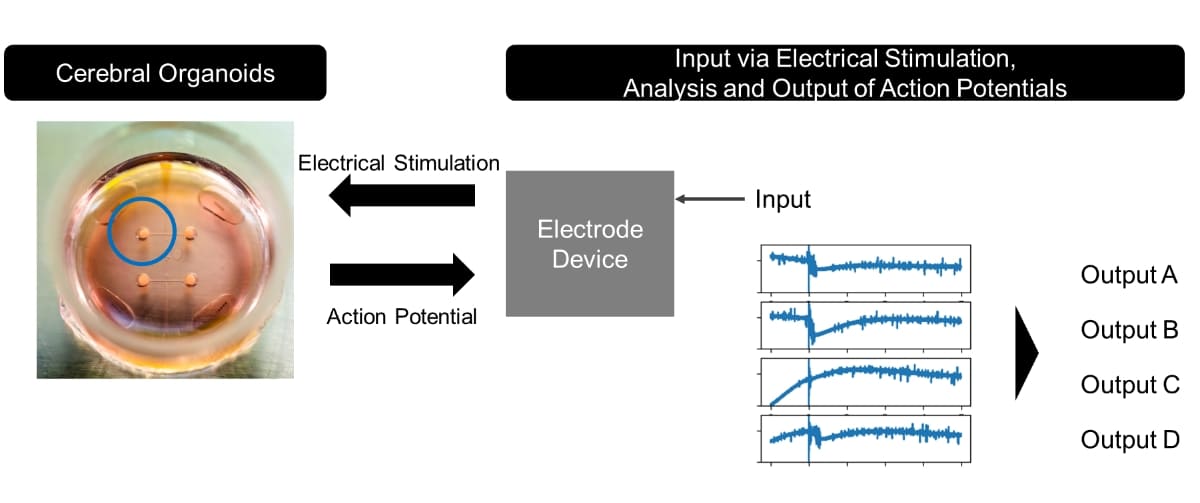
This leads to the question: can these characteristics of the human brain be applied to computing? SoftBank Corp.’s (TOKYO: 9434) Research Institute of Advanced Technology and The University of Tokyo investigated the possibilities by conducting joint research on next-generation computing technology using cerebral organoids – three-dimensional tissue culture models that partially replicate the structure of brain tissue.
Learn more about their findings in this deep dive.
(Posted on February 4, 2025)
by SoftBank News Editors