Eleven years ago on March 11, 2022, the Great East Japan Earthquake struck the Tohoku region of Japan. In the aftermath of this tragic event, many valuable lessons were learned, including how mobile phones are a lifeline that people use to gather information and to check up on their friends and family. Other types of natural disasters, such as flooding and typhoons, also underline the importance of mobile network resilience. Fully recognizing its responsibility as a provider of vital telecommunications infrastructure, SoftBank Corp. (TOKYO: 9434) is working to build a disaster-resilient communication network that can rapidly recover from disasters.
Here is a short introduction to some of SoftBank’s countermeasures.
Communication network initiatives

To provide telecommunication services around the clock, SoftBank is thoroughly strengthening its communication network with the following measures.
- Earthquake proofing at network center facilities
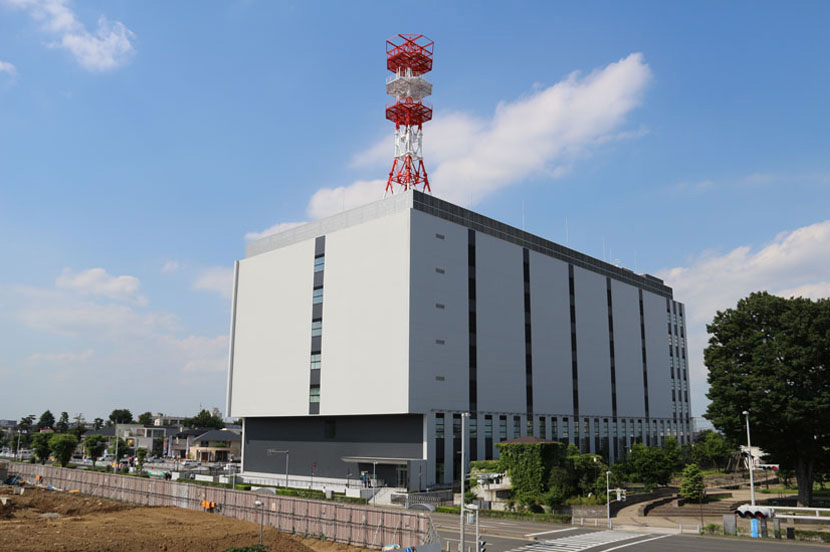
After the Great East Japan Earthquake in March 2011, the seismic resistance of network center facilities, which form the core of SoftBank’s telecommunications network, were reinforced to withstand a seismic intensity of 7 on the Japanese scale, an intensity where massive cracks appear on the ground. One of SoftBank’s major network centers is equipped with uninterruptible power sources and emergency power generators, and power outage countermeasures have been implemented to ensure the center can operate for 48 to 72 hours after a power outage.
- Transmission network constructed in ring form

SoftBank’s nationwide network has a redundant configuration so the East Japan and West Japan areas mutually back each other up. The transmission line network is also constructed in a ring configuration, so even if an equipment failure occurs at one location, connections can be rerouted.
- Base stations with increased resilience for continuous operation
In the event of a power outage due to a large-scale natural disaster, base stations typically lose power, and communications are disrupted as a result. As a power outage countermeasure, SoftBank’s base station facilities are equipped with power supply facilities that can maintain electrical power for more than 24 hours. Base stations serving essential facilities such as government offices and disaster relief medical facilities are equipped with generators capable of supplying power for 72 hours or more.
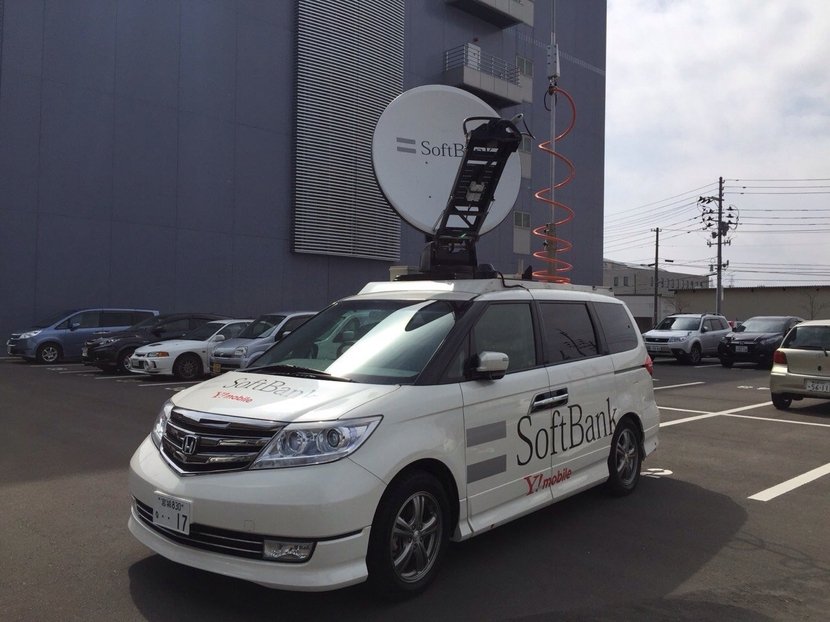
- Equipment for communication restoration deployed across Japan
SoftBank has 282 mobile satellite antennas available for use when optical fiber lines connected to base stations are cut. SoftBank also has at the ready approximately 100 mobile base station vehicles and 200 portable base stations, including those that can be mounted on vehicles.
- Disaster drills conducted in cooperation with local governments and agencies

To ensure a prompt response in the event of a large-scale disaster, SoftBank regularly conducts disaster readiness drills in cooperation with local governments, Japan’s Ground Self Defense Force, the Ministry of Defense, and the Japan Coast Guard. SoftBank participates in drills that involve loading supplies for the Self Defense Forces and Japan Coast Guard, as well as drills organized by local governments, to ensure smooth communication and cooperation when a disaster occurs.
Establishing systems to promptly restore communication services
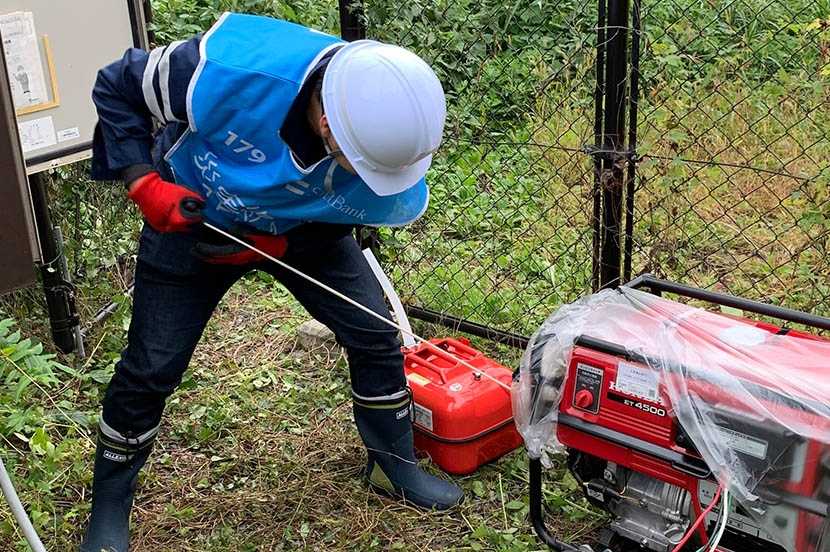

In the event of an emergency, SoftBank establishes an Emergency Response Department according to the extent of the damage so it can implement immediate recovery measures in an affected area. Building on its past experience with large-scale disasters, SoftBank now organizes disaster task forces ahead of forecastable disaster events, such as typhoons or torrential rains.
In addition to restoring telecommunication services, SoftBank also provides on-site support in affected areas. A total of approximately 1,500 satellite and mobile phones can be provided free-of-charge to local governments and other organizations for use as a means of communication in affected areas and for rescue and recovery activities. In addition, to support evacuation centers, mobile phones, fixed-line phones, Wi-Fi equipment, and recharging facilities are installed free of charge to ensure people have connectivity to confirm the safety of others and gather recovery-related information.
SoftBank's Disaster Preparedness and Recovery Support
SoftBank is also promoting the use of Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) solutions as a backup for ground-based networks when they get disrupted.
NTN solutions provide communication networks from space and the stratosphere. In the future, when ground-based communication facilities and networks are disrupted by earthquakes, tsunamis, and other natural disasters, a High Altitude Platform Station (HAPS) aircraft could be deployed the affected area to restore connectivity. As NTN solutions are not affected by events on the ground, they show great promise as a disaster countermeasure.
SoftBank's recovery measures have continued to evolve over the years since the Great East Japan Earthquake, and the company's efforts to utilize NTN solutions for disaster management have just begun. SoftBank will continue to promote these and other countermeasures so people can communicate safely and get support in the event of a disaster.
(Posted on March 18, 2022, Original article posted on March 9, 2022)
by SoftBank News Editors